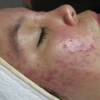
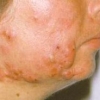
Trattamento delle cicatrici atrofiche del viso provocate dall'acne vulgaris, con laser Q-Switched Nd:YAG (neodimio: ittrio-alluminio-granato) a lunghezza d'onda di 1064 nm
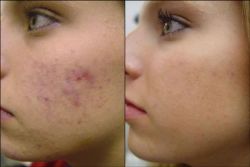 Il laser Q-Switched Nd: YAG (1064 nm) è una nuova modalità che è stata segnalata per la sua efficacia nel trattamento delle cicatrici da acne.
Il laser Q-Switched Nd: YAG (1064 nm) è una nuova modalità che è stata segnalata per la sua efficacia nel trattamento delle cicatrici da acne.
Obiettivo. Valutare l'efficacia e la sicurezza di questo laser nel trattamento delle cicatrici da acne.
Pazienti e metodi. Questo studio descrittivo e comparativo di una serie di casi, è stato condotto all'Al-Najaf Teaching Hospital di Kufa, in Iraq da ottobre 2010 a ottobre 2011. Sono stati inclusi nello studio un totale di 16 pazienti con cicatrici facciali da acne, in grado da lieve a moderato; 10 di loro hanno completato lo studio. Tutti i pazienti presentavano un tipo III di pelle secondo la scala Fitzpatrick. I pazienti sono stati divisi in due gruppi A e B e sono stati trattati con due diverse fluenze di energia: 5 J/cm2 per il gruppo (A) e 15 J/cm2 per il gruppo (B). Per ogni paziente sono state eseguite cinque sessioni di trattamento ad intervalli di 2 settimane e tutti sono stati seguiti per 6 mesi. Il miglioramento è stato valutato con metodi oggettivi e soggettivi.
Risultati. I cambiamenti nei punteggi dell'acne, in entrambi i gruppi, sono stati statisticamente insignificanti dopo 6 mesi di follow-up. Solo due pazienti si sono dichiarati soddisfatti del miglioramento dopo il trattamento: un paziente per ogni gruppo. Non sono stati segnalati gravi effetti collaterali.
Conclusione. Il laser Q-Switched Nd:YAG (1064 nm) può essere utilizzato nel trattamento di cicatrici atrofiche facciali causate dall'acne vulgaris.
Storia della pubblicazione:
Titolo: Treatment of atrophic facial scars of acne vulgaris by Q-Switched Nd:YAG (Neodymium: Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet) laser 1064 nm wavelength.
Rivista: J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2012 Oct;14(5):224-33.
Autori: Maluki AH, Mohammad FH.
Affiliazioni: College of Medicine, University of Kufa , Al-Najaf , Iraq.
Abstract:
Abstract Background. Q-Switched Nd:YAG laser (1064 nm) is a new modality that was reported to be effective in treatment of acne scars. Objective. To evaluate the effectiveness and the safety of this laser in treatment of acne scars. Patients and methods. This case series, descriptive and comparative study was conducted in Al-Najaf Teaching Hospital of Kufa Medical College, Iraq from October 2010 to October 2011. A total of 16 patients having mild to moderate facial acne scars were enrolled; 10 of them completed the study. All patients had Fitzpatrick skin type III. They were divided into two groups A and B and were treated with two different energy fluences: 5 J/cm2 for group (A) and 15 J/cm2 for group (B). Five treatment sessions with 2-week intervals were done for all patients and were followed up for 6 months. The improvement was evaluated by objective and subjective methods. Results. Changes in acne scores in both groups were statistically insignificant after 6 months follow-up. Only two patients were satisfied with the improvement after treatment- one patient from each group. No serious side effects were reported. Conclusion. Q-Switched Nd:YAG laser (1064 nm) can be used in treating atrophic facial scars of acne vulgaris.
https://www.youtube.com/@djfdm