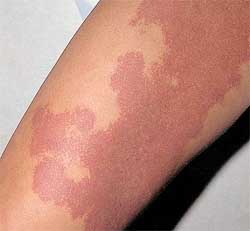
Gli effetti avversi della terapia fotodinamica (PDT) per il trattamento delle voglie a macchia vino porto (PWS)
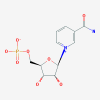
 Diversi studi cinesi suggeriscono che la terapia fotodinamica (PDT) mediata dall'emoporfirina rappresenti un trattamento alternativo per le voglie a macchia vino porto (PWS). OBIETTIVO:
Diversi studi cinesi suggeriscono che la terapia fotodinamica (PDT) mediata dall'emoporfirina rappresenti un trattamento alternativo per le voglie a macchia vino porto (PWS). OBIETTIVO:
Valutare le risposte terapeutiche e gli effetti avversi associati alla PDT con emoporfirina per il trattamento e la gestione delle PWS. METODO: Sono state esaminate retrospettivamente le cartelle cliniche di 700 pazienti che hanno subito un trattamento di PDT nel nostro centro. Sono stati rivisti anche gli effetti negativi e le reazioni correlate al trattamento.
RISULTATO:
Diversi tipi di lesioni PWS e individui diversi hanno mostrato altrettante risposte immediate (ad esempio il gonfiore, il cambiamento di colore, il dolore): da un certo punto di vista, queste reazioni sono state un utile indicatore dell'endpoint del trattamento. L'edema e la formazione di croste sono state le reazioni più comuni del post-trattamento. Gli effetti avversi a breve termine (come le bolle, la dermatite eczematosa, la fotosensibilità cutanea) e a lungo termine (come il cambiamento della pigmentazione, la formazione di cicatrici) sono stati causati generalmente dalla fototossicità associata alla combinazione di un fotosensibilizzatore e dell'esposizione alla luce.
CONCLUSIONE:
Anche se la PDT rappresenta un trattamento alternativo e sicuro per le voglie a PWS, i parametri di trattamento devono essere selezionati per ciascun paziente e, durante l'irradiazione, devono essere monitorati i cambiamenti della pelle in modo da ridurre al minimo il rischio di reazioni avverse. Infatti, la sovrastima del dosaggio di luce richiesta o l'incapacità di riconoscere i cambiamenti cutanei associati agli effetti avversi possono aumentare il rischio di un esito sfavorevole.
Storia della pubblicazione:
Titolo: Adverse effects associated with photodynamic therapy (PDT) of port-wine stain (PWS) birthmarks.
Rivista: Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2012 Dec;9(4):332-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 Apr 17.
Autori: Yuan KH, Gao JH, Huang Z.
Affiliazioni:Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Nanfang Hospital of South China Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Abstract:
BACKGROUND: Several Chinese studies suggest that Hemoporfin-mediated photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an alternative treatment for port-wine stain (PWS) birthmarks. OBJECTIVE: To evaluate treatment responses and adverse effects associated with Hemoporfin PDT for the treatment of PWS and their management. METHOD: The medical records of 700 patients who underwent PDT treatment in our center were retrospectively examined. Treatment-related reactions and adverse effects were reviewed. RESULT: Different types of PWS lesions and different individuals showed different immediate responses (e.g. swelling, color change, pain). To certain extents these reactions were a useful indicator of the treatment endpoint. Edema and scabbing were the most common post-treatment responses. Short-term (e.g. blister, eczematous dermatitis, cutaneous photosensitivity) and long-term (e.g. pigmentation change, scar formation) adverse effects were generally caused by the phototoxicity associated with the combination of photosensitizer and light exposure. CONCLUSION: Although PDT is a safe treatment alternative for PWS birthmarks, treatment parameters must be selected for each individual patient and cutaneous changes must be monitored during light irradiation to minimize the risk of adverse effects. Over estimation of required light dosage or failure to recognize cutaneous changes associated with adverse effects can increase the risk of a poor outcome.