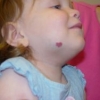
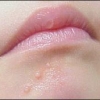
Confronto punto per punto del trattamento con terapia fotodinamica (PDT) e con dye laser pulsato (PDL) per le voglie a macchia vino porto (PWS)
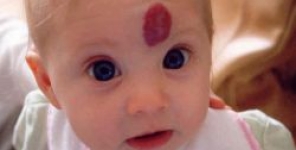
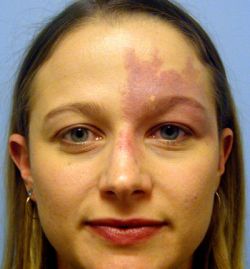 La fototermolisi mediata dal dye laser pulsato (PDL) è il trattamento standard di base per le voglie a macchia vino porto (PWS). La terapia fotodinamica (PDT) con bersaglio vascolare potrebbe essere un'alternativa per il trattamento della PWS. Lo scopo di questo studio è stato quello di confrontare i risultati clinici del trattamento PDT con quello PDL.
La fototermolisi mediata dal dye laser pulsato (PDL) è il trattamento standard di base per le voglie a macchia vino porto (PWS). La terapia fotodinamica (PDT) con bersaglio vascolare potrebbe essere un'alternativa per il trattamento della PWS. Lo scopo di questo studio è stato quello di confrontare i risultati clinici del trattamento PDT con quello PDL.
Metodi: Due lesioni PWS piatte e adiacenti sono state selezionate tra 15 pazienti (2 maschi e 13 femmine, tra gli 11-36 anni) e sono state assegnate in modo casuale ad una singola sessione di PDL e di PDT, rispettivamente. Il PDL è stato effettuato con un laser pulsato di 585 nm. Il PDT è stata eseguito con una combinazione di etere monometilico di ematoporfirina (HMME) e con un laser di bassa potenza a vapori di rame (510.6 nm e 578.2 nm). I risultati clinici sono stati valutati colorimetricamente e in modo visivo, durante il follow-up.
Risultati: Sono state trattate 9 lesioni PWS di colore rosso e 6 lesioni PWS viola. Per le PWS rosse, la valutazione colorimetrica ha mostrato che il tasso di sbiancamento di PDL e di PDT a 2 mesi è variato dall'8% al 24% e dal 22% al 55%, rispettivamente. Per le PWS viola, lo sbiancamento di PDL e di PDT è variato dall'8% al 33% e dal 30% al 45%, rispettivamente. In generale, c'è stata una differenza significativa tra l'effetto sbiancante di una singola sessione di PDL e di una singola sessione di PDT.
Conclusioni: Questo confronto ha dimostrato che PDT è almeno altrettanto efficace quanto PDL e, in alcuni casi, addirittura superiore. Il vero valore di PDT per il trattamento delle PWS merita ulteriori indagini.
Storia della pubblicazione:
Titolo: Side-by-side comparison of photodynamic therapy (PDT) and pulsed dye laser (PDL) treatment of port-wine stain (PWS) birthmarks
Rivista: British Journal of Dermatology. doi: 10.1111/bjd.12130
Autori: K. Gao, Z. Huang, K.-H. Yuan, B. Zhang, Z.-Q. Hu
Affiliazioni: Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Nanfang Hospital of South China Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Laser Plastic and Aesthetic Center, Liuhuaqiao Hospital, Guangzhou, China
Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Colorado Denver, CO USA
Abstract:
Background: Pulsed dye laser (PDL)-mediated photothermolysis is the current standard treatment of port-wine stain (PWS) birthmarks. Vascular-targeted photodynamic therapy (PDT) might be an alternative for the treatment of PWS. The aim of this study was to compare clinical outcomes of PDT and PDL treatment.
Methods: Two adjacent flat PWS lesions were selected from 15 patients (2 males and 13 females; 11-36 years old) and randomly assigned to single session PDL and PDT, respectively. PDL was delivered by a 585 nm pulsed laser. PDT was carried out by a combination of hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether (HMME) and low power copper vapour laser (510.6 nm and 578.2 nm). Clinical outcomes were evaluated colorimetrically and visually during follow-up.
Results: A total of 9 red PWS lesions and 6 purple PWS lesions were treated. For red PWS, colorimetrical assessment showed that the blanching rate of PDL and PDT at 2 months ranged from -11% to 24% and 22% to 55%, respectively. For purple PWS, that of PDL and PDT ranged from 8% to 33% and 30% to 45%, respectively. Overall, there was a significant difference between the blanching effect of single session PDL and single session PDT.
Conclusions: This side-by-side comparison demonstrates that PDT is at least as effective as PDL and in some cases, superior. The true value of PDT for the treatment of PWS deserves further investigation.