Terapia depigmentante con laser Q-switched Nd:YAG per la vitiligine universale
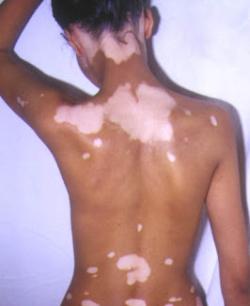 Qualsiasi pigmento residuo nei pazienti con vitiligine universale è gestito con trattamenti topici, crioterapia o laser. Obiettivo:
Qualsiasi pigmento residuo nei pazienti con vitiligine universale è gestito con trattamenti topici, crioterapia o laser. Obiettivo:
Lo studio si propone di valutare l'efficacia e la sicurezza del laser Q-switched Nd:YAG per il trattamento della pigmentazione residua nei pazienti con vitiligine universale. Materiali e Metodi:
Quindici pazienti con vitiligine universale resistenti ai trattamenti topici e con pigmentazione residua del viso, delle mani e dei piedi, sono stati trattati con sedute singole o multiple del laser Q-switched Nd:YAG. I trattamenti topici sono stati proseguiti anche tra una seduta e l'altra e la depigmentazione raggiunta è stata monitorata attraverso gli esami clinici e le ripetute fotografie digitali. La risposta al trattamento è stata etichettata come eccellente — se il pigmento residuo si era ridotto di almeno il 90% — mentre è stata etichettata come risposta parziale se la pigmentazione veniva ridotta solo del 50-90%. Inoltre, sono stati monitorati gli effetti negativi del trattamento.
Risultati:
Tredici pazienti dei 15 inizialmente inclusi nello studio hanno mostrato un'eccellente risposta al trattamento. Altri due pazienti hanno mostrato una scarsa risposta, con una riduzione della pigmentazione minore del 50%. Il numero di sedute laser necessarie in ciascun sito è stato variabile da 1 a 3, e mai più di tre sedute per ciascun sito. Da parte dei pazienti, non sono stati riportati eventi avversi significativi.
Conclusioni:
La pigmentazione residua nei pazienti con vitiligine universale, che non rispondono alle sole opzioni di trattamento topico, possono essere gestiti in modo abbastanza efficace con il laser Q-switched Nd:YAG, senza significativi eventi avversi.
Storia della pubblicazione:
Titolo: Depigmentation therapy with Q-switched Nd: YAG laser in universal vitiligo
Rivista: Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery
Autori: Imran Majid, Saher Imran
Affiliazioni:Department of Dermatology, Government Medical College; CUTIS Skin and Laser Institute, Srinagar, Kashmir, India CUTIS Skin and Laser Institute, Srinagar, Kashmir, India
Abstract:
Background: Any residual pigment left in patients of universal vitiligo is managed with topical treatments, cryotherapy, and lasers. Aim: The study aims to assess the efficacy and safety of Q-switched Nd: YAG laser in treating the residual pigmentation in patients with universal vitiligo. Materials and Methods: Fifteen patients of universal vitiligo with residual pigmentation on the face, hands, or feet, resistant to topical treatments, were treated with single or multiple sessions of Q-switched Nd: YAG laser treatment. Topical treatments were continued in between the laser sessions and the depigmentation achieved was monitored by clinical examination and repeat digital photographs. Response to the treatment was labelled as excellent if the residual pigment could be reduced by at least 90% while 50-90% resolution of pigmentation was labelled as a partial response. Adverse effects to the treatment offered were also monitored. Results: Thirteen of the 15 patients enrolled for the study showed an excellent response to the treatment offered. Two other patients showed a poor response with less than 50% resolution of pigmentation. The number of laser sessions needed at a particular site ranged from 1 to 3 and no patient was offered more than three sessions of laser treatment at any site. No significant adverse events were reported by any patient. Conclusions: Residual pigmentation in patients with universal vitiligo that does not respond to topical treatment options alone can be managed quite effectively with Q-switched Nd: YAG laser without any significant adverse effects.