Il tiosolfato di sodio per il trattamento della calcifilassi non-uremica
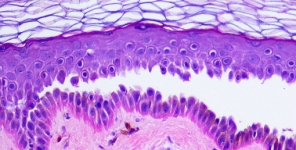
 La calcifilassi è una vasculopatia indotta dalla calcificazione metastatica che provoca l'occlusione dei piccoli vasi sanguigni. Sebbene la calcifilassi sia normalmente associata con la malattia renale allo stadio terminale, si possono verificare anche dei casi di calcifilassi non-uremica, e nonostante i riscontri continuino ad aumentare non è stato ancora stabilito un trattamento standard per questa malattia. Il sodio tiosolfato (STS), che è stato efficace per il trattamento della calcifilassi uremica, si dimostra promettente anche per la calcifilassi non-uremica ma i dati a disposizione sono tuttora limitati. In questo articolo, descriviamo un caso di calcifilassi non-uremica in un paziente con funzione renale e paratiroidea normale che ha avuto una completa risoluzione della malattia dopo trattamento con STS, e passiamo in rassegna i casi simili nel lavoro pubblicato. Sulla base dei risultati positivi descritti in questa serie di casi, l'STS sembra essere una terapia efficace per il trattamento della calcifilassi non-uremica.
La calcifilassi è una vasculopatia indotta dalla calcificazione metastatica che provoca l'occlusione dei piccoli vasi sanguigni. Sebbene la calcifilassi sia normalmente associata con la malattia renale allo stadio terminale, si possono verificare anche dei casi di calcifilassi non-uremica, e nonostante i riscontri continuino ad aumentare non è stato ancora stabilito un trattamento standard per questa malattia. Il sodio tiosolfato (STS), che è stato efficace per il trattamento della calcifilassi uremica, si dimostra promettente anche per la calcifilassi non-uremica ma i dati a disposizione sono tuttora limitati. In questo articolo, descriviamo un caso di calcifilassi non-uremica in un paziente con funzione renale e paratiroidea normale che ha avuto una completa risoluzione della malattia dopo trattamento con STS, e passiamo in rassegna i casi simili nel lavoro pubblicato. Sulla base dei risultati positivi descritti in questa serie di casi, l'STS sembra essere una terapia efficace per il trattamento della calcifilassi non-uremica.
Storia della pubblicazione:
Titolo: Sodium thiosulfate in the treatment of non-uremic calciphylaxis
Rivista: The Journal of Dermatology. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12139
Autori: Matthew S. Ning, Kathryn M. Dahir, Emily H. Castellanos, Laura Y. McGirt
Affiliazioni:Division of Dermatology, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, USA Division of Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, USA Department of Medicine, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, USA
Abstract:
Calciphylaxis is a metastatic calcification-induced vasculopathy that results in the occlusion of small blood vessels. Although calciphylaxis is normally associated with end-stage renal disease, calciphylaxis from non-uremic origin occurs as well. While the number of reports continues to increase, a standard treatment for non-uremic calciphylaxis has yet to be established. Sodium thiosulfate (STS), which has been proven to be effective in the treatment of uremic calciphylaxis, shows promise; however, reports of its use in non-uremic cases are limited. We describe a case of non-uremic calciphylaxis in a patient with normal renal and parathyroid function who had complete resolution of disease after treatment with STS, and we review similar cases in the published work. Based on the successful outcomes detailed in this case series, STS appears to be an effective therapy for non-uremic calciphylaxis.