Cidofovir intralesionale per il trattamento delle verruche cutanee virali, multiple e recalcitranti
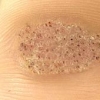
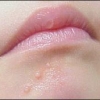
 Il cidofovir è un analogo nucleoside della deossicitidina con una forte attività contro un ampio spettro di virus a DNA, incluso il papillomavirus umano. Il primo obiettivo è stato quello di valutare l'efficacia del cidofovir per il trattamento delle verruche cutanee virali, recalcitranti dopo le terapie convenzionali o dove l'approccio chirurgico è difficile per la loro posizione o estensione.
Il cidofovir è un analogo nucleoside della deossicitidina con una forte attività contro un ampio spettro di virus a DNA, incluso il papillomavirus umano. Il primo obiettivo è stato quello di valutare l'efficacia del cidofovir per il trattamento delle verruche cutanee virali, recalcitranti dopo le terapie convenzionali o dove l'approccio chirurgico è difficile per la loro posizione o estensione.
In secondo luogo, gli autori si sono proposti di evidenziare i possibili effetti collaterali locali e sistemici, conseguenti al trattamento. Duecentottanta pazienti affetti da verruche cutanee virali recalcitranti, sono stati trattati con cidofovir intralesionale di 15 mg/mL una volta al mese.
Gli autori hanno dichiarato che i candidati erano già stati sottoposti prima ad almeno altri due trattamenti riportati nelle linee guida per la gestione delle verruche cutanee virali. In 276 casi, le verruche sono completamente scomparse: 158 di questi hanno avuto un periodo di follow-up superiore a 12 mesi e 118 hanno avuto un periodo di follow-up di 6 mesi. In media, sono state sufficienti 3,2 iniezioni per risolvere il problema.
Gli effetti collaterali locali consistevano nel dolore e nella sensazione di bruciore durante le iniezioni; sono stati osservati prurito, eritema, e iperpigmentazione post-infiammatoria. Non sono stati notati casi di effetti collaterali sistemici.
Il trattamento è stato ben tollerato, e le verruche sono completamente scomparse senza ripresentarsi. Il cidofovir intralesionale sta emergendo come una valida alternativa terapeutica per le verruche che non rispondono ai trattamenti convenzionali.
Storia della pubblicazione:
Titolo: Intralesional cidofovir for the treatment of multiple and recalcitrant cutaneous viral warts
Rivista: Dermatologic Therapy. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8019.2012.01477.x
Autori: Paolo Broganelli, Antonella Chiaretta, Barbara Fragnelli, Maria Grazia Bernengo
Affiliazioni: Department of Oncology and Dermatology, University of Turin, Turin, Italy
Abstract:
Cidofovir is a nucleoside analog of deoxycytidine with a strong activity against a broad spectrum of DNA viruses, including human papillomavirus. The first objective was to evaluate efficacy of cidofovir for the treatment of cutaneous viral warts, recalcitrant after conventional therapies or where the surgery approach is difficult for their location or extension. Second, the present authors propose to point out possible local and systemic side effects consequent to treatment. Two-hundred eighty patients affected by recalcitrant cutaneous viral warts, were treated with intralesional cidofovir 15 mg/mL once a month. The present authors stated that candidates were those who had made before at least two other treatments reported in the guideline for management of cutaneous viral warts. In 276 cases, warts completely cleared: 158 of those have a follow-up period longer than 12 months and 118 have a follow-up of 6 months. On the average, 3,2 injections were enough to solve the problem. Local side effects consisted of pain and burning sensation during the injections; itching, erythema, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation were observed. No cases of systemic side effects were noted. The treatment was well tolerated, and the warts were completely cleared without relapses. Intralesional cidofovir is emerging as an effective therapeutic alternative for warts that are unresponsive to conventional treatments.